
Natural musiclistening at its very best.
In developing the ERGO Headphones an extensive study of the human anatomy and acoustical properties of the ear and head was considered essential to the total design process. These studies showed that there was no purpose in the ERGO design to follow the herd by developing just an other headphone.
To achieve high quality, distortion-free music reproduction and maximum user comfort, with absence of listener fatigue, a headphone of unconventional design was the only solution

A) The ERGO headphone rests lightly on top of the head, the weight, mere ounces, distributed over a large insensitive surface. This light weight and soft foam headband
cushion result in complete freedom of pressure and allow the scalp to “breathe” naturally.
B) A foam strip, at the rear of each speaker panel, rests lightly behind each ear. These do not contact the ears to cause any deformation, which would obstruct the natural
created by the speakers
C) The speaker panels are fixed in the correct position to maintain optimum vertical and horizontal angles of sound dispersion
D) Since the speaker panels do not physically contact the ears, the intervening spaces permit a fresh air-flow from below the ears, which avoids the heat, perspiration and listener fatigue so commonly experienced with conventional headphones. Conventional headphones distort the shape of the outer ear and pump sound directly into the auditory canal depriving the ear of its natural function. Such headphones may have a wide frequency response, but by contacting and deforming the ear they lose or distort the second (indirect) soundwave information resulting in unnatural sound reproduction and listener fatigue.
In addition, by pressing the ears against the head or enclosing them completely, conventional headphones cause discomfort by closing off the free circulation of air around the ears, i.e. nature’s heat exchange system. ERGO headphones reproduce sounds, in a manner quite unlike other headphones free of colouration or distortion, clean and natural. Their unique quality of design and construction ensure sounds superior to that of many speakers on the market. With ERGO headphones, you can listen to music for extended periods of time without being conscious of wearing headphones and without the usual fatigue associated with conventional headphones.
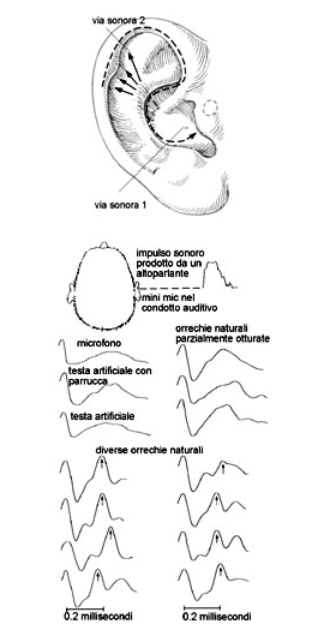
THE ACOUSTICAL FUNCTION OF THE EARLOBE:
The perceived sound information is divided by the “Anthelix” into two parts. The first part is going directly, from the edge of the “Anthelix”, into the auditory canal. The other part of the sound information is diverted to the entrance of the “Helixtunnel” then follows through this tunnel and only then will it reach the auditory canal. The distance of this soundwave is appr. 66 mm. or 0.2 milliseconds time delay. Everyone can convince himself, by obstructing the way of the 2nd sound-wave with his fingers.
This experiment confirms the theory of the two soundwaves. The test has been done in the following way: A square-wave of 0.14 milliseconds has been reproduced through a loudspeaker placed 90 degrees on the side to the test object. A mini-microphone, which does not obstruct Helix the edge of the auditory canal, has been placed into the different models. The first, direct sound-wave remains the same with all the models. The 2nd, indirect soundwave however, changes dramatically from the models to the natural ears, in which the 2nd soundwave is also very pronounced. (nearly as strong as the 1st sound-wave.)
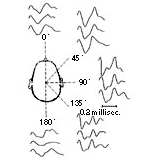
THE HORIZONTAL SOUND LOCALISATION WITH ONE EAR.
The intensity of the first, direct sound-wave changes depending on the angle of dispersion of the sound, with the 2nd indirect soundwave, this change is much more marked. The ideal angle of sound dispersion should therefore be between 45 and 90 degrees.
By watching people with a defect in hearing one can notice that they turn their head to the source in such a way that they can receive the soundwaves in the optimal angle. i.e. between 45-90 degrees.
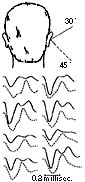
THE VERTICAL SOUND LOCALISATION WITH ONE EAR.
The reception of sound originating 30 degrees over the edge of the auditory canal shows the second information as quite flat, where as with reception of sound originating 45 degrees below the edge of the auditory canal, shows a sharp peak, different from each persons ear. The displacement of the indirect 2nd sound-wave in time delay is a factor, also the intensity and form of the 2nd soundwave changes dramatically. The optimal angle of dispersion of sound should be between the two (30° above and 45° below
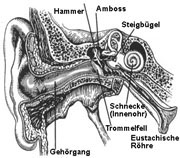
THE EAR.
The sound passes through the auditory canal and then reaches the eardrumm. Here the mechanical charge is transfered with the “hammer”, “anvil” and “stirrup” to the inner ear “snail”. The auditory nerves or “palpate cells” are distributed in the following manner in the inner ear. Near the larger opening we find the auditory nerves for the high frequencies and at the end the ones for the low frequency. Herewith, one can explain, why an overload of the ear, with low frequencies will damage the hearing of high frequencies first.

The Jecklin OSS disc is used more and more often for optimal shooting. The handling is simple. Even amateurs can make good recordings. You will need 2 good omnidirectional microphones and possibly a microphone stand.
The Jecklin Float headphones are no longer manufactured, but spare parts are still available from us.
